Difference Between Good Fats and Bad Fats: Explained
Published: 28 Dec 2025
Understanding fats is one of the most important steps in building a healthier lifestyle. Most people grow up hearing “fat is bad,” but that’s not true at all. Your body needs fat, just not every kind. Some fats protect your heart, improve your skin, balance your hormones, and support your brain. Others slow your system down, raise unhealthy cholesterol, and trigger inflammation.
This guide will walk you through the difference between good fats and bad fats in a clear, simple way. You’ll learn what each fat does inside your body, how to tell them apart, how to use good fats daily, and how to avoid the bad ones without feeling restricted.
Let’s start by understanding why fats matter in the first place.
Why Your Body Needs Fat
Even if you want to lose weight or stay lean, removing all fats from your diet can harm your health.

Fat plays several essential roles:
- It gives you long-lasting energy
- It protects your organs
- It keeps your skin and hormones balanced
- It supports your brain (which is 60% fat)
- It helps your body absorb vitamins A, D, E, K
- It keeps you full and reduces cravings
The real goal is not to avoid fat, but to choose the right type.
Difference Between Good Fats and Bad Fats (Short Overview)
To make things easy to understand:
Good Fats = Healthy for your heart and body
These fats protect your health and should be part of your daily meals.
Bad Fats = Harmful when eaten often
These fats damage your heart health and increase cholesterol.
Now let’s break everything down in detail.
GOOD FATS (Healthy Fats)
These fats support your heart, mind, hormones, skin, and metabolism. There are two types of good fats:
- Monounsaturated Fats
- Polyunsaturated Fats (includes Omega-3 & Omega-6)
Let’s explain each in detail.
1. Monounsaturated Fats
These fats are known as “heart-friendly fats.” They help reduce bad cholesterol (LDL) and increase good cholesterol (HDL). They also help your body manage blood sugar levels better.
What they do inside your body:
- Reduce the risk of heart diseases
- Keep your arteries clean
- Support brain function
- Reduce cravings by keeping you full
- Reduce inflammation
Foods rich in monounsaturated fats:
- Avocados
- Olive oil
- Nuts (almonds, cashews, peanuts)
- Seeds
- Peanut butter
- Sesame oil
How to add them daily:
- Cook your meals with olive oil instead of vegetable oil
- Add avocado slices to toast, eggs, or salads
- Keep a handful of nuts as a daily snack
- Use hummus or nut butter as spreads
2. Polyunsaturated Fats
These fats are essential — meaning, your body cannot make them. You must get them from food. There are two major types:
A. Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Very Good Fat)
This is one of the most powerful fats for your body.
What Omega-3 does:
- Protects your heart
- Improves memory and brain function
- Reduces inflammation
- Supports joint health
- Improves mood and reduces anxiety
Foods rich in Omega-3:
- Fatty fish: salmon, sardines, trout
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
- Walnuts
- Fish oil supplements (optional)
How to add them daily:
- Add chia seeds to yogurt
- Use flaxseed powder in smoothies
- Eat salmon 1–2 times a week
- Snack on walnuts
B. Omega-6 Fatty Acids (Good — But Needs Balance)
Your body also needs Omega-6 fats, but in the right amount. Too much can increase inflammation. A small balanced amount is healthy.
Omega-6 rich foods:
- Sunflower oil
- Corn oil
- Soybean oil
- Walnuts
- Sesame seeds
Key rule: Omega-3 and Omega-6 should be balanced. Most people eat too much Omega-6 and not enough Omega-3. A simple fix — add more Omega-3 foods.
BAD FATS (Unhealthy Fats)
These fats harm your heart, slow digestion, and increase inflammation. There are two main types:
- Saturated Fats (Bad in excess)
- Trans Fats (Worst fat — avoid completely)
Let’s understand each.
1. Saturated Fats
Saturated fats become solid at room temperature. Your body can handle them in small amounts, but too much can raise LDL (bad cholesterol).
What too much saturated fat does:
- Increases risk of heart disease
- Causes artery blockage
- Raises unhealthy cholesterol
- Causes inflammation
Foods high in saturated fats:
- Butter
- Ghee (in excess; small amounts okay)
- Full-fat cheese
- Cream
- Red meat (beef, lamb, mutton)
- Processed meats
Safe rule: You don’t need to remove saturated fats completely. Just keep them limited and balanced with good fats.
2. Trans Fats (The Worst Fat)
Trans fats are the most dangerous type of fat. They are industrial fats created to make food last longer.
What trans fats do to your body:
- Raise bad cholesterol (LDL)
- Lower good cholesterol (HDL)
- Increase heart disease risk
- Trigger weight gain, belly fat, and inflammation
- Increase the risk of diabetes
Foods containing trans fats:
- Fried fast foods (zinger, fries, nuggets)
- Margarine
- Commercial baked items (donuts, pastries, biscuits)
- Packaged chips
- Ice creams
- Frozen fried snacks
Rule: Avoid trans fats completely. There is no safe limit.
How to Tell Good Fats and Bad Fats Apart
Here’s a simple way to remember:
✔ Good fats = come from whole foods
(Avocados, nuts, fish, seeds, olive oil)
✘ Bad fats = come from processed or fried foods
(Fast food, packaged snacks, commercial baking)
✔ Good fats support your body
✘ Bad fats stress your body
How Much Fat Should You Eat Daily?
You don’t need to count every gram.
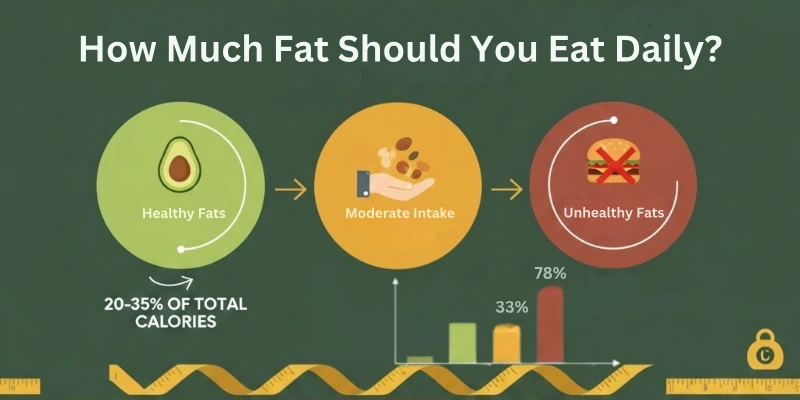
Focus on this:
- Add more good fats
- Limit saturated fats
- Avoid trans fats
A healthy daily plate looks like this:
✔ 1–2 tbsp olive oil
✔ A handful of nuts
✔ Some seeds
✔ One avocado a few times weekly
✔ Fatty fish twice weekly
This balance supports your heart, hormones, brain, and energy levels.
How to Replace Bad Fats with Good Fats
Here are easy swaps:
| If you eat this… | Replace with this… |
| Butter | Olive oil or avocado oil |
| Mayonnaise | Greek yogurt or avocado |
| Fried chicken | Baked or air-fried chicken |
| Packaged chips | Nuts or seeds |
| Creamy sauces | Hummus or yogurt-based dips |
| Margarine | Real butter (small amount) |
Small swaps make long-term changes without feeling restricted.
Good Fats for Weight Loss
Good fats help with weight control because they:
- Keep you full longer
- Reduce cravings
- Balance hormones
- Support stable energy
Avocados, nuts, seeds, eggs, and salmon are excellent for healthy weight balance. Bad fats do the opposite by slowing metabolism and storing belly fat.
Good Fats for Skin, Hair & Hormones
Your skin loves good fats because they keep it hydrated. Omega-3 helps reduce acne, dryness, and aging.
Good fats:
- Improve skin glow
- Reduce hair fall
- Balance hormones
- Support a healthy menstrual cycle
Bad fats cause breakouts, oily skin, hair thinning, and hormonal imbalance.
Good Fats for Brain Health
Your brain is made mostly of fat, so good fats help you:
- Think clearly
- Memorize better
- Stay focused
- Reduce anxiety
Salmon, walnuts, chia seeds, dark chocolate, and olive oil are great choices. Bad fats reduce mental clarity and increase inflammation in the brain.
Final Note
Understanding the difference between good fats and bad fats changes the way you look at food forever. When you choose good fats daily, you support your heart, mind, hormones, and energy. When you cut down bad fats, you protect your long-term health.
Small steps, small swaps, and small improvements today create the healthiest version of you tomorrow.
FAQs: Good vs Bad Fats
Here are some of the most commonly asked questions related to the comparison between good fats and bad fast:
Your body needs good fats to make hormones, support brain health, and absorb vitamins. They give you steady energy and keep you full longer. Good fats also protect your heart and reduce inflammation.
Not all saturated fats are harmful. Small amounts from natural foods like eggs or milk are okay for most people. The problem comes from eating them in large amounts or from processed sources. Balance is the key.
Bad fats raise bad cholesterol and block your arteries over time. They make your heart work harder to pump blood. This increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Cutting them reduces long-term risk.
Yes, good fats keep you full and stop unnecessary snacking. They help your body burn fat more effectively. But you still need moderate portions because fats are high in calories. Pair them with whole foods for best results.
Many baked goods, fries, margarine, and packaged snacks hide bad fats. They are found even in foods that look healthy, like flavored yogurt or crackers. Reading labels helps you avoid them. Look for “hydrogenated oil” to spot trans fats.
Olive oil is safe for medium heat cooking. At very high heat, it can lose nutrients and flavor. For frying or high heat, use avocado oil instead. Use olive oil for sautéing or drizzling.
Use good fats from nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil. Reduce fried foods, processed snacks, and bakery items. Choose grilled or baked meals instead of deep-fried versions. Small swaps daily make a big difference.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks